3d printing filament comparison chart guide
Are you new to 3D printing and wondering which filament to use for your project? With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one.
3D printing has become increasingly popular in recent years, and with it, the demand for different types of filaments has grown too. Each filament has its unique properties and benefits, making it essential to know which one will work best for your project.
Choosing the right filament is an important aspect of 3D printing. It affects the quality, strength, and appearance of your printed object. With a wide range of materials to choose from, including ABS, PLA, PETG, and more, it can be confusing to know which one to use for a specific project.
To help you make an informed decision, we have created a comprehensive 3D printing filament comparison chart guide. This guide will provide you with all the necessary information about different filaments, their properties, strengths, and weaknesses, making it easier for you to choose the right one for your project. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of 3D printing filaments.
What is 3D printer filament?
3D printer filament is a material used in 3D printing. It is usually made from thermoplastics, such as ABS or PLA, and can be purchased in a variety of colors and sizes. The filament is heated up and then extruded through the print head of the 3D printer. As it cools, the layer-by-layer process is completed to create the 3 D object.
Different types of 3D printing filament
There are many different types of 3D printing filaments available, each with its own unique properties and benefits. The most common types are ABS, PLA, PETG, Nylon, and TPU. Let’s take a closer look at the characteristics and uses of each:
ABS (Acrylon itrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is a strong and flexible plastic filament that is commonly used for industrial applications. It can be printed at higher temperatures and offers good impact resistance.
PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic made from renewable resources, such as corn starch or sugar cane. It’s easy to use, but not as strong or durable as ABS.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate): PETG is a strong, durable thermoplastic that can be printed at a lower temperature than ABS and PLA. It has good impact resistance and is often used for outdoor applications.
Nylon: Nylon is a strong, flexible plastic filament that is commonly used for items such as tools and mechanical parts] TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is a flexible plastic filament that is often used for items such as phone cases and shoe soles. It offers good impact resistance and can be printed at lower temperatures than other filaments.
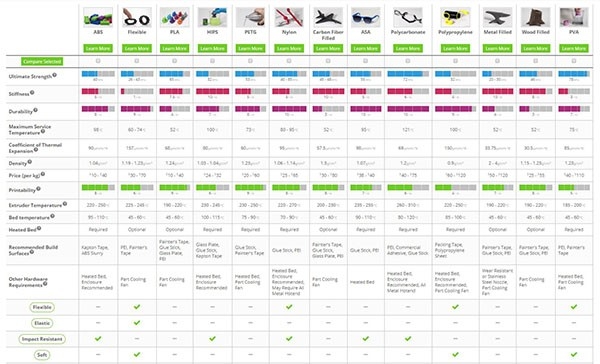
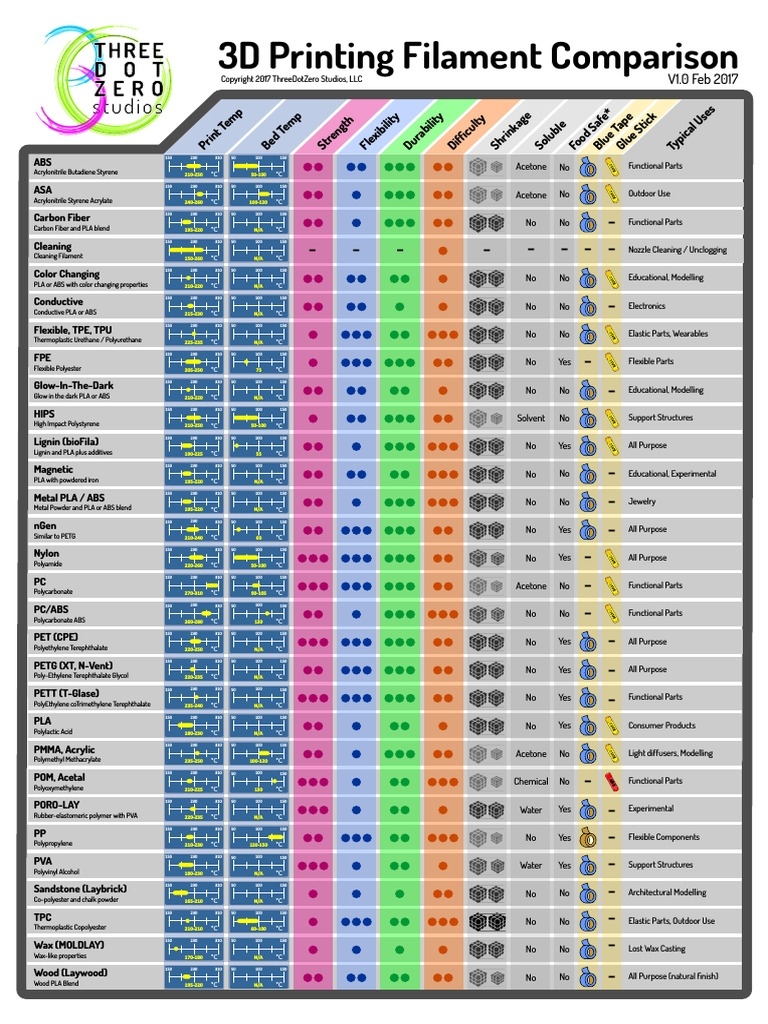
3D Printing Filament Comparison Chart Guide
Using a 3D printing filament comparison chart guide is the best way to quickly compare the various types of filaments available and make an informed decision about which one to use for your project.
The chart will provide you with all the necessary information, such as type, properties, temperature range, strength and flexibility, shrinkage and warping rates, cost, and more. This makes it easy to compare different filaments and determine which one will work best for your project.
What is the best 3D printer filament?
The best 3D printer filament is largely dependent on the type of project that you’re creating. For example, if you’re looking to print a phone case or other items that need flexibility and impact resistance, then TPU would be a good option.
On the other hand, if you’re looking for something with good strength and durability, then ABS may be a better choice. Additionally, PLA is a good option for those looking for an eco-friendly filament. Ultimately, the best 3D printer filament will depend on your specific project needs.
When it comes to selecting the right 3D printing filament for your project, it is important to consider all aspects of the material. Each filament has its own unique characteristics and properties that may be better suited for some projects than others. To ensure you get the best possible results, consider these factors when making your choice:
Print Temperature – Different filaments require different print temperatures, so make sure to check the recommended temperature range for the filament you are considering.
Strength and Flexibility – The strength and flexibility of a filament will vary depending on the type of material, so make sure to take these factors into account when making your selection.
Shrinkage and Warping Rates – Different filaments may have different shrinkage and warping rates, so be sure to research these before making your decision.
Cost – Consider the cost of the filament in relation to the quality and properties it offers.
By researching all these factors, you can make an informed decision about which 3D printing filament is best for your project. With the help of a 3D printing filament comparison chart, you can easily compare different types of filaments and choose the one that works best for you.
Cheap vs expensive filaments
When it comes to 3D printing filaments, there can be a huge difference in price between the cheap and expensive options. Generally speaking, the cheaper filaments tend to offer lower quality and fewer features than their more expensive counterparts.
Cheaper filaments may not have as many features or be as durable or strong as the more expensive ones. In addition, they may not offer the same level of detail or accuracy when printing. For this reason, it is important to consider both the cost and quality of a filament before making your decision.
On the other hand, more expensive filaments tend to offer higher quality and more features. These filaments are usually better suited for intricate designs or projects that require high levels of detail or strength. They may also provide more consistent results with less shrinkage and warping.
Ultimately, the best filament for you will depend on your budget and project needs. If you’re looking for a cheap option, then the cheaper filaments may be suitable for basic designs or projects. However, if you require higher quality or intricate designs, then the more expensive filaments may be worth investing in.
Where to buy 3d printing filaments?
When it comes to buying 3D printing filaments, there are a variety of online stores and retailers that offer a wide range of options. Some popular retailers include Amazon, MatterHackers, and 3D Printer Filament Depot. You can also check out your local electronics store or hobby shop for additional options.
When shopping for 3D printing filaments, it is important to consider the type of filament you need, the quality of the material, and your budget. You should also make sure to read reviews and compare prices before making your purchase.
When selecting a 3D printing filament, it is important to research the type of material you need and its associated properties. Different filaments will have varying levels of strength, flexibility, and shrinkage rates. Additionally, different printers may require different print temperatures for optimal results. It is also essential to consider the cost in relation to the quality and features offered by each filament. A 3D printing filament comparison chart can be a useful tool in helping you make an informed decision.