Is 3d printing safe indoors
3D printing has revolutionized the world of manufacturing, allowing individuals and small businesses to create custom objects with ease. However, as with any new technology, questions about the safety of 3D printing have been raised.
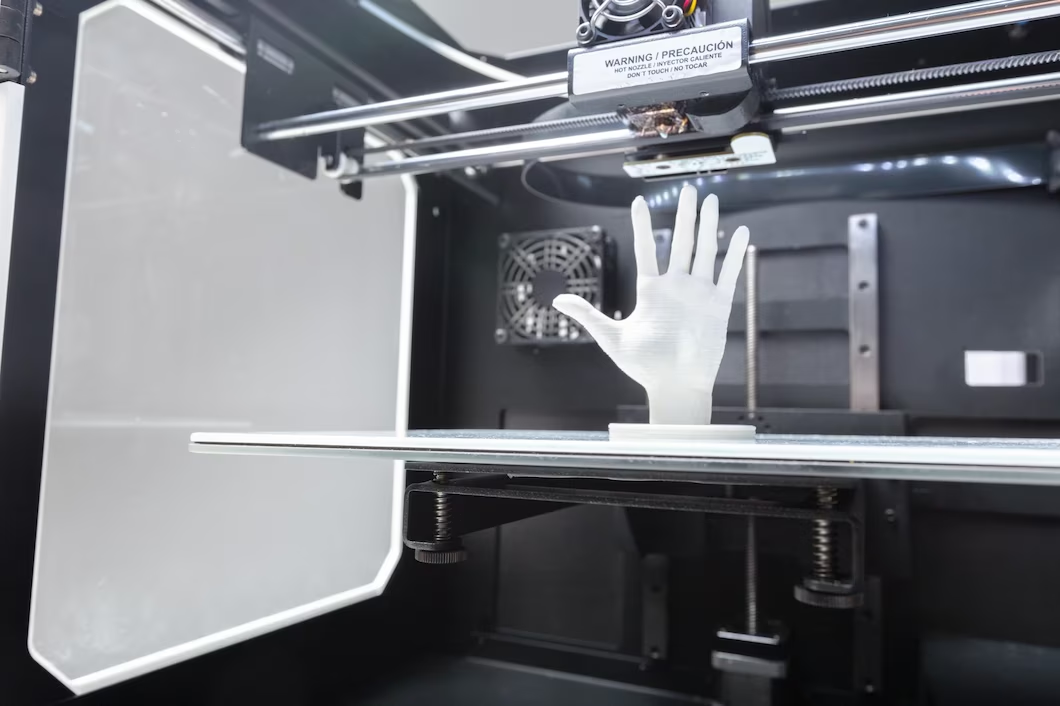

With the rise of home 3D printing, concerns about the potential health and safety hazards of the process have come to the forefront. Some worry that the chemicals and materials used in the printing process could be harmful to humans, particularly if the printing is done indoors.
Before investing in a 3D printer for home use, it’s essential to understand the potential health and safety risks involved. In this article, we’ll explore the question of whether 3D printing is safe indoors, examining the risks and precautions you should take to protect yourself and your family.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing is an innovative process of making three-dimensional solid objects from a digital file. The process uses additive manufacturing, where successive layers of material are laid down in different shapes to create the final object.
3D printing has been used in a variety of industries, including engineering, automotive and medical, to create products with complex geometries and intricate designs that would be impossible or too costly to create through traditional manufacturing processes.
3D printing offers tremendous advantages over traditional manufacturing, allowing designers to quickly produce prototypes or even final products with a fraction of the cost and time. Additionally, it also allows for greater customization when producing parts or products since each component can be tailored to fit specific needs and requirements.
Although 3D printing is relatively safe indoors, it is still recommended to follow safety guidelines such as wearing protective gear and using proper ventilation when operating the printer.
Is 3D Printing Safe Indoors?
3D printing offers tremendous advantages over traditional manufacturing and is quickly becoming a popular choice for producing parts or products. However, it is important to consider the safety of 3D printing when operating indoors.
In general, 3D printing is safe when used in a well-ventilated area, as the fumes from melted plastic can be hazardous if inhaled. It is also recommended to use protective gear while using the printer and avoid contact with hot surfaces or objects that have recently been printed.
Additionally, users should always ensure that their 3D printer is properly calibrated and all components are securely fastened before operation. With these safety guidelines in mind, 3D printing can be done safely indoors without any health risks to those nearby.
Types of 3D Printers
3D printing is an innovative manufacturing process that has revolutionized the way many products are manufactured. There are various types of 3D printers available on the market, each suited to different tasks and applications. Fused filament fabrication (FFF) is the most common type of 3D printer and uses thermoplastic filaments which are heated, melted, and extruded onto a build plate in order to create objects.
Stereolithography (SLA) printers use ultraviolet lasers to harden liquid resin into solid shapes layer by layer. Selective laser sintering (SLS) involves powder particles being fused together using a focused laser beam, while direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) prints metal parts layer by layer.
Finally, digital light processing (DLP) uses an array of LEDs to project an image onto a vat of photopolymer resin in order to form solid parts. Depending on the application or material being used, any one of these types of 3D printers can be used to produce high-quality results.
FDM Printers
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is a type of 3D printer that works by melting thermoplastic filament and extruding it onto a build plate to create objects. This method allows for the creation of complex shapes in a variety of materials such as PLA, ABS, PETG and nylon.
FDM printers are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of 3D printers and are incredibly versatile, making them ideal for home users. They can also be used for industrial applications such as prototyping and tooling. The main benefit of FDM is its speed; it is one of the fastest methods for creating objects with complex geometries.
Additionally, FDM offers greater control over layer thickness, allowing parts with fine details to be printed quickly and accurately. With the right settings, FDM produces high-quality prints that can rival those from more expensive 3D printing techniques such as SLA or SLS.
SLA/DLP Printers
Stereolithography (SLA) and digital light processing (DLP) are two of the most popular types of 3D printing available today. SLA printers work by curing a liquid photopolymer layer-by-layer using ultraviolet (UV) light.
This method produces highly accurate parts with excellent surface finish quality and resolution. DLP is similar to SLA in that it uses UV light, but instead of shining through a mask as in SLA, it shines directly onto an entire layer at once. This results in faster print speeds than SLA, though the accuracy and surface finish may be slightly lower due to the lack of fine control over individual layers.

Both methods are ideal for producing small, detailed parts with intricate geometries that would be difficult or impossible to make with other manufacturing processes. They are also incredibly safe for indoor use since no fumes or hazardous materials are released during the printing process.
SLS Printers
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is a type of 3D printing technology that uses a high-powered laser to fuse together small particles of plastic, metal, ceramic, or glass powder.
SLS printers can produce parts with intricate geometries and complex internal structures that are nearly impossible to create with traditional manufacturing methods.
What sets them apart from other 3D printing technologies is the fact that they don’t require any supports or post-processing steps like sanding or polishing. The result is a strong and durable part with excellent surface finish quality and accuracy.
Best of all, these printers are incredibly safe for indoor use since no hazardous materials are released during the printing process. SLS has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its versatility and ability to produce parts quickly and cost-effectively.
Commonly Used Filaments and Resins
Filaments and resins are two of the most commonly used materials in 3D printing. Filaments are thermoplastic materials that are extruded through a heated nozzle to create a 3D object. Commonly used filaments include ABS, PLA, nylon, and PETG.
These materials come in a variety of colors, making them an ideal choice for creating colorful prints with intricate details and textures. Resins are liquid photopolymers that are cured and hardened by ultraviolet light or laser.
They can be used to create high-resolution prints with exceptional accuracy and surface finish quality. Commonly used resins include epoxy, polyurethane, rubber-like elastomers, and dental resins.
Both filaments and resins have their own advantages and disadvantages depending on the application requirements. As such, it is important to determine which material best suits your project before beginning your 3D printing journey.
ABS Filament
ABS filament is one of the most popular materials used in 3D printing due to its versatility and reliability. This thermoplastic material is sturdy, flexible and easy to print with, making it a great choice for both experienced and novice 3D printer users alike.
ABS filament has excellent mechanical properties such as high impact resistance and strength, making it ideal for creating functional parts that need to withstand wear and tear. It also offers excellent thermal stability which allows it to maintain its shape even when subjected to extreme temperatures.
Another advantage of ABS filament is its ability to be post-processed with acetone vapor smoothing or sanding techniques in order to achieve a glossy finish. While more expensive than PLA filament, ABS provides better quality prints with greater durability compared to other filaments on the market.
PLA Filament
PLA filament is a popular 3D printing material due to its low cost and ease of use. PLA filament is made from renewable resources, such as corn, which makes it a great eco-friendly option for 3D printing. PLA prints at lower temperatures than other materials, making it easy to use even with basic 3D printers.
Its low melting temperature also means that PLA filament does not produce strong odors when printing indoors. It has good strength and rigidity, making it an ideal choice for prototyping or creating parts that do not need to withstand heavy wear and tear.
However, PLA is not as durable as ABS filament and can be brittle if exposed to extreme temperatures or moisture. Despite this, PLA still remains a great choice for those looking for an affordable 3D printing material with minimal environmental impact.