What causes spaghetti 3d printing?
Have you ever heard of 3D printed spaghetti? It may sound bizarre, but it’s actually happening. So what causes spaghetti 3D printing?
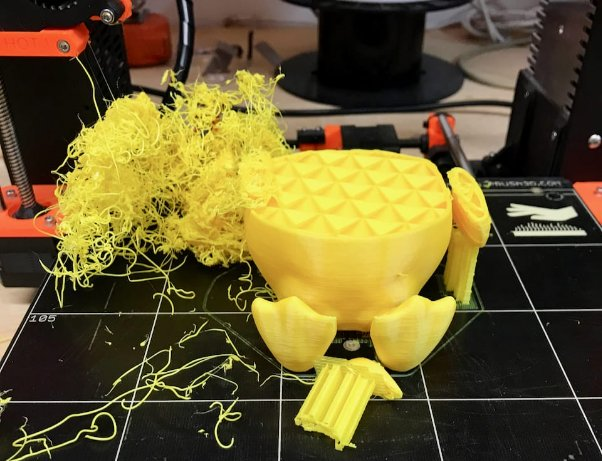

3D printing has come a long way since its inception in the 1980s. Currently, it is possible to print complex structures such as prosthetic limbs, aircraft parts, and even food. And yes, that includes spaghetti.
Spaghetti 3D printing is a fascinating concept that has captured the attention of engineers and foodies alike. But what exactly causes the unique texture and shape of 3D printed spaghetti? In this article, we’ll explore the science behind it and why it’s an exciting development in the world of 3D printing.
What is spaghetti 3D printing?
Spaghetti 3D printing, also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is an innovative additive manufacturing technique that uses a plastic filament to construct three-dimensional objects. The plastic filament is fed into a heated nozzle and extruded layer by layer onto a flat surface.
This process allows for the creation of intricate details and complex geometries with minimal human involvement. It’s a relatively new technology compared to other 3D printing technologies and has quickly become popular due to its affordability, accessibility, and fast production time.
The main advantage of spaghetti 3D printing is that it produces strong parts with high detail at low cost. It can produce complex parts in various materials such as PLA, ABS, PETG, Nylon, TPU, HIPS and PVA without the need for expensive tools or equipment.
Additionally, spaghetti 3D printing requires little post-processing since the parts can be printed directly on the build plate without any further support structures or additional finishing steps. This makes it ideal for rapid prototype design and product development projects.
In conclusion, spaghetti 3D printing is a great tool for quick prototyping and product development due to its low cost and high detail capabilities while requiring minimal post-processing steps. With its increasing popularity among hobbyists and professionals alike, it’s no wonder why this technology is becoming so popular in the world of additive manufacturing!
Causes of spaghetti 3D Printing
The causes of spaghetti 3D printing can be attributed to a number of factors. First, the availability of low-cost and easy-to-use 3D printers have made it possible for anyone to create objects with intricate details and complex geometries without the need for expensive tools or equipment.
Second, the variety of materials that are available for use in this type of printing has increased significantly over the years, allowing users to explore new possibilities with their designs. Finally, advances in software development have allowed for faster design iterations and improved accuracy in 3D printing projects. These factors have all contributed to the growing popularity of spaghetti 3D printing among hobbyists and professionals alike.
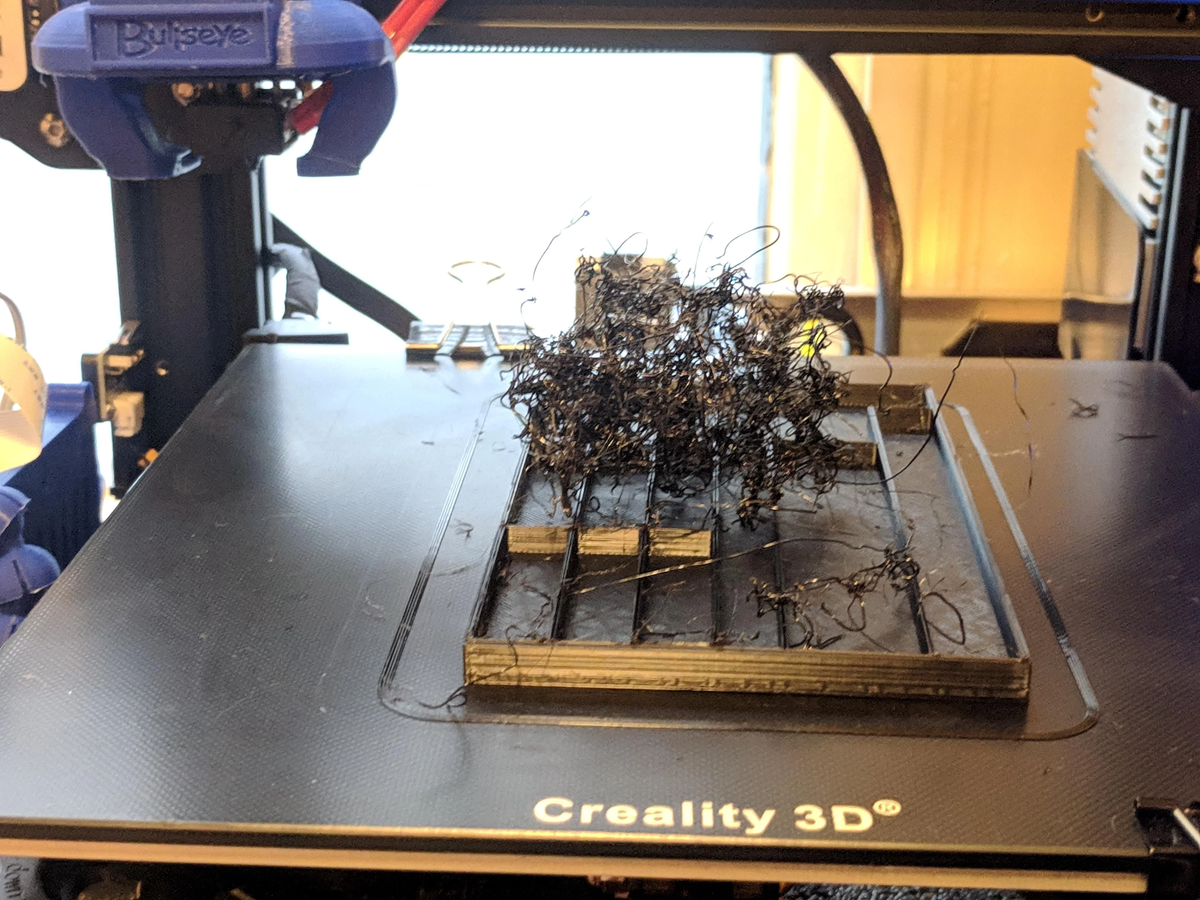
Print Head Issues
Print head issues are one of the most common problems encountered when using a 3D printer. These issues can lead to poor quality prints and wasted materials, as well as time spent troubleshooting and replacing parts.
The most common causes of print head issues include clogged nozzles, incorrect nozzle temperatures, a damaged or bent filament feeder, and an obstructed path for the extruded material. In order to prevent these problems from occurring, users should ensure that their 3D printer is clean and in good working order before each use.
Furthermore, it is important to regularly inspect the print head for any dirt or debris that may be blocking the nozzle or preventing filament from flowing properly. Finally, correct calibration of the printhead is essential for achieving quality prints and avoiding costly repairs.
Nozzle Diameter & Height
Nozzle diameter and height are two important factors that must be taken into consideration when 3D printing. The nozzle size affects the resolution of the print, as a larger nozzle will produce coarser prints while a smaller one will create finer details. Additionally, the nozzle height can affect how much filament is extruded by the printer and how quickly it is done.
To ensure optimal results, it is important to use the correct nozzle size for your material and adjust its height accordingly. If you are using a filament with a wide range of diameters, such as spaghetti plastic, you may need to experiment with different nozzle sizes and heights to find the best combination for your project.
It is also important to maintain proper maintenance on your 3D printer’s nozzles, as dirt or dust buildup can block them and prevent proper filament flow. Taking these factors into account should help you create successful 3D prints with your machine.
Excessive Temperature
Excessive temperature is a common issue when 3D printing, as it can cause the filament to melt too quickly and lead to poor results. If the temperature is too low, the plastic won’t melt properly and will not adhere correctly to the build plate. On the other hand, if it’s too high, it can lead to warping or stringing of your prints.
To avoid these problems, it is important to make sure that you’re using the proper extrusion temperature for your specific material. This can be found on their respective data sheets or through trial and error. Additionally, make sure that your heated bed isn’t set higher than necessary as this could result in excess temperatures as well. If everything else fails, you can also purchase a thermocouple or thermistor which will measure temperatures more accurately and help you adjust them accordingly.
Lack of Retraction Settings
Retraction settings are a key part of 3D printing as they help prevent stringing and oozing. Retraction is the process of retracting the filament back into the nozzle before it moves to a new location. This helps reduce blobs, strings, and oozing between layers.
Without retraction, your print will be full of imperfections that can cause it to fail or not look its best. To ensure good results with your prints, make sure you adjust your retraction settings correctly for each material you use. Generally, you should have a retraction speed of around 30-50 mm/s and a distance of 1-4mm depending on the material being used.
You may also need to adjust other parameters such as coasting or wiping depending on the type of filament you’re using. If you do not have proper retraction settings optimized for your printer, it’s likely that your prints won’t turn out well.
Poor Quality Print Head
Poor quality print heads can be a major issue when it comes to 3D printing. A print head is the component of the printer that actually deposits the molten plastic onto the build plate, and if it’s not up to snuff, then you’re likely to experience poor quality prints.
Poor quality print heads are often made from low-grade materials, which can lead to clogging or jamming. The blockage of these components can also cause inconsistencies in extrusion, resulting in uneven layers and imperfections in your prints.
The best way to avoid this issue is to purchase a high-quality printer with a reliable print head. That said, if you have an existing printer with a low-quality head, there are ways to improve performance by cleaning and calibrating it regularly.
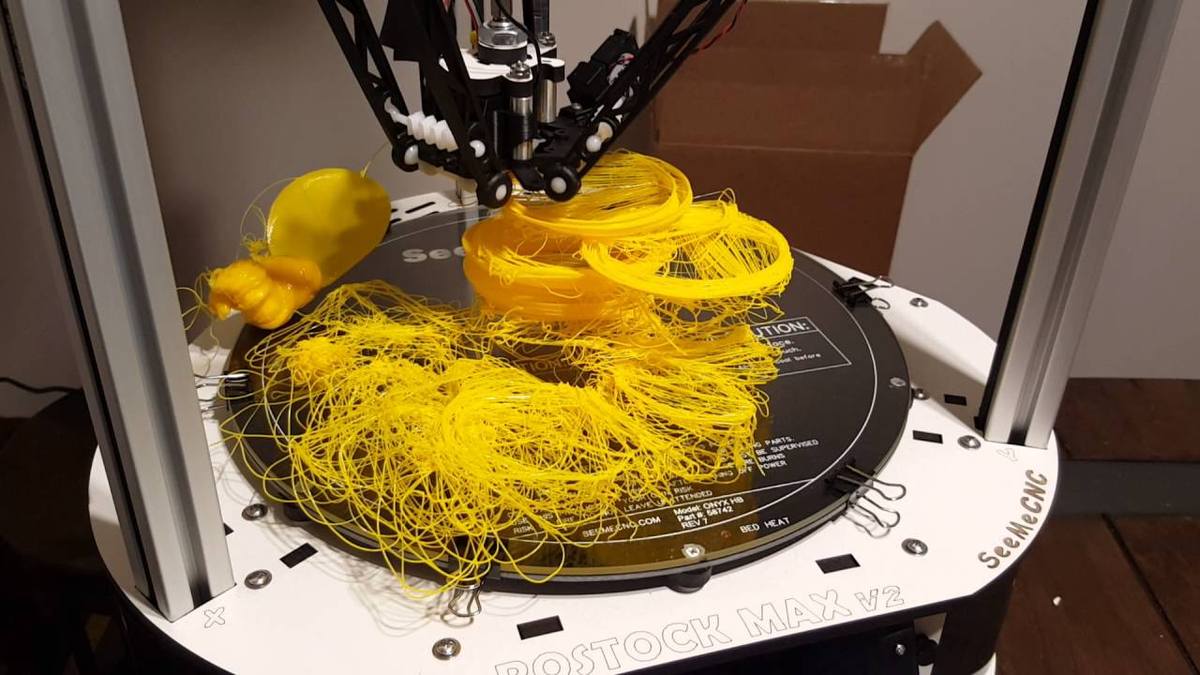

To do this properly, you should make sure that all of the moving parts are lubricated with the correct type of lubricant and that everything is tightened properly so that nothing slips while printing. If you take care of your printer’s print head, it will provide better results and help you achieve those perfect 3D prints!